REGARDING YOUR OWN PERFORMANCE
1. What were the three aspects of the assignments I've submitted that I am most proud of? The compendium reviews and the list of species.
2. What two aspects of my submitted assignments do I believe could have used some improvement? The labs on the fertility rate one as I wasnt sure if I even did it right.
3. What do I believe my overall grade should be for this unit? I believe my grade should be A-B. I worked really hard on this unit. I spent many hours on the Compendium reviews and researching the species and writing about each one.
4. How could I perform better in the next unit? I always say this but its always true, start working a little earlier on everything that way I won't have to work so late into the night.
REGARDING THE UNIT
At what moment during this unit did you feel most engaged with the course? Looking up each and everyone of the species. I feel that it made me learn a lot about different species.
At what moment in the unit did you feel most distanced from the course? During the fertility lab because it was really confusing.
What action that anyone (teacher or student) took during this unit that find most affirming and helpful?
What action that anyone (teacher or student) took during this unit did you find most puzzling or confusing? On the List of species lab I got confused on how many of the species I was actually suppose to write about so I may have written about more than I needed to because just wasn't clear on it.
What about this unit surprised you the most? How the species have a different role in our ecosystem and how important these different roles are.
Friday, July 25, 2008
Thursday, July 24, 2008
List of Species 20-30
20: Scientific Name: Turnicidae
Common Name: Quail
21: Scientific Name Polecat
Common Name Polecat
22: Scientific Name Turdus Merula
Common Name Black Bird
23: Scientific Name Parkinsonia
Common Name Pala Verde
24: Scientific Name Felis Catus
Common Name Cat
25: Scientifc Name Oryctolagus cuniculus
Common Name Rabbits
26: Scientific Name Cervus canadensis
Common Name Elk
27: Scientific Name Zenaida macroura
Common Name Dove
28: Scientific Name Phasianus colchicas
Common Name Pheasant
29 Scientific Name Gopherus Agassizi
Common Name Desert Tortoise
30: Scientific Name Castor canadensis
Common Name Beaver
Common Name: Quail
21: Scientific Name Polecat
Common Name Polecat
22: Scientific Name Turdus Merula
Common Name Black Bird
23: Scientific Name Parkinsonia
Common Name Pala Verde
24: Scientific Name Felis Catus
Common Name Cat
25: Scientifc Name Oryctolagus cuniculus
Common Name Rabbits
26: Scientific Name Cervus canadensis
Common Name Elk
27: Scientific Name Zenaida macroura
Common Name Dove
28: Scientific Name Phasianus colchicas
Common Name Pheasant
29 Scientific Name Gopherus Agassizi
Common Name Desert Tortoise
30: Scientific Name Castor canadensis
Common Name Beaver
Species #20
.jpg) Scientific name- Crotalus afrox
Scientific name- Crotalus afroxCommon name- Western Diamondback Rattlesnake
Rattlesnakes hibernate in caves or burrows.
Adult specimens have no natural predators. Hawks, eagles and other snakes have been known to prey on young rattlesnakes.
Rattlesnakes are a key participant in the food web of many small rodents, rabbits and birds. In turn the rattlesnake is preyed upon by a variety of larger mammals and birds.
Rattlesnakes are not domesticated species.
Species #19
 Scientific Name: Coccinella septempunctata
Scientific Name: Coccinella septempunctataCommon Name: Lady Bug/Lady Beetle
Lady bugs are most commonly known as beneficial insects. Both adults and larvae feed on many different soft bodied insects with aphids (plant lice) being their main food source.
Lady bugs are very valuable to our eco-system because they control pests.
I believe that Lady bugs are domesticated because they can be considered humans best friend by working like a pesticide to kill pests.
Species #18
 Scientific name- Streptococcus Bacteria
Scientific name- Streptococcus BacteriaCommon name- Strep throat
Strep throat is a micro organism
The bacteria that cause strep throat tend to hang out in the nose and throat, so normal activities like sneezing, coughing, or shaking hands can easily spread infection from one person to another.
I believe that strep throat is domesticated because it is part of the human body.
Species #17
 Scientific name- Felis Catus Cats Cynodon
Scientific name- Felis Catus Cats CynodonCommon name- Bermuda grass
Bermuda grass is a major turf species for sports fields, lawns, parks and golf courses. It can also be a serious weed in many crops being a vigorous growing grass. It is a difficult weed to eradicate because of its seed production and deep rhizomes. Bermuda grass is a food source to many species.
I believe Bermuda grass is domesticated because humans control where it is planted and it is around our homes.
Species #16
 Scientific Name: Voles
Scientific Name: VolesCommon Name: Mouse
The most common mouse is the common house mouse. It is found almost all over the world, and is used as a laboratory mouse because it serves as a model organism in biology. It is also a popular pet. Mice living in the wild usually only live up to 5 months due to heavy predation. Cats, wild dogs, foxes, birds of prey, snakes, and certain insects have been known to prey heavily upon mice. Mice can be harmful pests, damaging crops, and spreading diseases through there parasites and feces.
I believe that mice are domesticated because they are used in laboratories and can be pets.
Species #15
 Common name- plaque
Common name- plaqueScientific name- supragingival chemical
Plaque is a sticky, colorless film of bacteria that forms on teeth. It makes them feel fuzzy to the tongue and is most noticeable when teeth are not brushed.
Plaque develops when food containing carbohydrates are left on the teeth.
Bacteria that lives in the mouth thrive on these foods-producing acids and over time these acids destroy tooth enamel.
Plaque formation can be provented by brushing teeth at least twice a day with tooth paste. Toothpaste will kill the plaque.
I believe plaque is domesticated because it is a bacteria that lives in the human body.
Species #14
 Scientific Name: Canis Lupis
Scientific Name: Canis Lupis Common Name: Dog
Dogs are domesticated subspecies of the wolf. Dogs are widely kept for working and as pets also in human history they are being used as a food source in some cultures. Dogs are very important to people by helping people who are blind, deaf, physically disabled. They also help the police catch the bad guys. They can sniff out illegal products, such as drugs, and things that have been smuggled into the United States of America. Other dogs that help humans are search and rescue dogs these dogs help find missing persons.
I believe that dogs are domesticated because they play a huge role in human lives each and everyday. Whether it be just as a loving friend or helping find missing people.
Species #13
 Common name: cattle
Common name: cattleScientific name: ungulates
of the family- Bovinae
Cattle are raised as livestock for meat, dairy products, and are used for pulling carts and plows. Cows interbreed with other closely related species.
Adult male- bull
Castrated male- steer
Young female before having a calf- heifer
Adult female that has had one or more calves- cow
Young cattle- calves
Cattle are domesticated because as livestock they are a source of food.
Species #12
 Common name: Hummingbirds
Common name: HummingbirdsScientific name: Apodiforms
Hummingbirds are specialized nectarivores. Many plants pollinated by hummingbirds produce flowers in shades of red, orange and bright pink. Although they will take nector from flowers of many colors. Hummingbird pollinated flowers produce weak nector containing high concentrations of sucrose whereas insect pollinated flowers produce nectars dominated by fuctose and glucose. With the exception of insects, hummingbirds while in flight have the highest metabolism of all animals. This is necessity to support the rapid beating of their wings. They typically consume more than their own weight in nectar a day so they must visit hundreds of flowers daily.
I don't believe hummingbirds are domesticated because humans do not interact with them.
Species #11
 Common name: mushroom
Common name: mushroomScientific name: Eumycotes
A Mushroom is produced by fungal organism. I have witnessed if we have alot of moisture on our grass and it is really humid, mushrooms will develop in the yard. Mushrooms acquire nutrients by breaking down dead organic matter including animal wastes. Mushrooms are decomposers and are valuable because they release inorganic substances that are taken up by plants.
Mushrooms are also a food source to other species including humans.
I think that mushrooms are domesticated because we eat them.
Species #10
 Common name: dust mites
Common name: dust mitesScientific name: Dermatophagoides Farinae
Dust mites are Detritus feeders, they feed on organic matter such as flakes of shed human skin. They flourish in the stable environment of dwellings. They can be killed by micro predators by exposure to direct sun rays.
Dust mites are the most common cause of asthma and allergic symptoms world wide.
I think dust mites are domesticated because they live in our homes with us even though we may not see them.
Species #9
 Common name: Green Algae
Common name: Green AlgaeScientific name: Chlorophytes
Green algae contains two forms of chlorophyll which captures light energy to fuel the manufacture of sugars. Algae is a photosynthetic organism meaning it produces most of the organic nutrients for the bisphere.Therefore it produces food in freshwater and marine habitats.
My dad thinks Algae is kinda a nuisance to try and control in our swimming pool but he continues to put chemicals in to control it.
I think algae is domesticated because it is all around us and probably sometimes we don't always see it.
Species #8

Scientific Name: Scorpinida
Common Name: Scorpions
Scorpions are an eight legged venomous invertebrate, they are related to spiders, mites, ticks and harvestmen. They ambush their pray lying in wait as they sense its approach. They eat all types of insects, spiders, centipedes, and other scorpions. Bigger scorpions may feed on vertebrates, such as smaller lizards, snakes, and mice. They capture their prey by their pedipalps, paralyzing them with their venom if it is necessary. The prey is then subjected to an acid spray that dissolves the tissues, that then allows the scorpion to suck up the remains. Not only are they predators they can also be prey eaten by creatures such as centipedes, tarantulas, insectivorous lizards, birds, and mammals. Bats hunt scorpions for food.
I believe that scorpions aren't domesticated.
Common Name: Scorpions
Scorpions are an eight legged venomous invertebrate, they are related to spiders, mites, ticks and harvestmen. They ambush their pray lying in wait as they sense its approach. They eat all types of insects, spiders, centipedes, and other scorpions. Bigger scorpions may feed on vertebrates, such as smaller lizards, snakes, and mice. They capture their prey by their pedipalps, paralyzing them with their venom if it is necessary. The prey is then subjected to an acid spray that dissolves the tissues, that then allows the scorpion to suck up the remains. Not only are they predators they can also be prey eaten by creatures such as centipedes, tarantulas, insectivorous lizards, birds, and mammals. Bats hunt scorpions for food.
I believe that scorpions aren't domesticated.
Species #7
 Common name: E coli
Common name: E coliScientific name: Escherichia coli
Most strains of E coli are harmless and lives in intestines of humans and animals. However, E. coli 0157:H7, is a powerful strain that produces a powerful toxin that can cause illness. An outbreak traced to this strain was caused by eating undercooked ground beef.
E coli is a bacteria and it acquires nutrients by breaking down dead organic matter. This bacteria helps our intestines break down waste.
I think that E coli would be domesticated because it lives within our bodies and we are accustomed to it being there.
Species #6

 Common name: honey bee
Common name: honey beeScientific name: Apis Mellifera
Bees are the most important pollinating insects, their interdependence with plants makes them an excellent example of the type of symbiosis known as mutualism, association between unlike organisms that is beneficial to both parties.
Bees are very important to human food supply because they pollinate plants which produces more plants.
Bees are not domesticated species.
Species #5
 Common Name: red fire ant
Common Name: red fire antScientific Name:Solenopsis invicta Buren
Ants are social insects and live in colonies or nests. New ant colonies are started by a single fertilized queen ant that lays eggs and tends her brood that develop into working ants. The worker than takes over tending the brood and may shift the brood from place to place as moisture and temperature fluctuate in the nest. Fire ants build mounds out of soil. When the mound is disturbed, ants emerge aggressively to bite and sting the intruder.
Ants are terrestrial detritus feeders meaning they feed on decomposing particles of organic matter. When they bite they spray acid which in a human feels similar to getting burned by fire.
Ants are not domesticated species and when they enter homes, are a nuisance to humans because they contaminate food.
Species #4
 Scientific Name: Arecaceae or Palma
Scientific Name: Arecaceae or PalmaCommon Name: Palm tree
Many common products and food are derived from palm. Palm trees are also widely used in landscaping for their exotic appearance making them one of the most economically important plants. Also symbols for idea as victory, peace and fertility.
I believe that Palm trees are domesticated because they are in many people's yards where the climate is ideal for them. Many parts of Arizona have palm trees because they like hotter temperatures. We have several of them in our yard. So the population of palm trees by way of selection have been domesticated.
Species #3

 Scientific Name: Prosopis
Scientific Name: ProsopisCommon Name: Mesquite Tree
The beans from the mesquite tree can be ground into flour to make bread and other bread like things. It also is full of nutrients for many animals. The Indian people and the Hispanic and Anglo settlers believed that the mesquites showed individuality, adaptability, opportunism, toughness and stubbornness.
I believe that the mesquite tree is domesticated because they have become accustomed to human control.
Humans co evolve with the mesquite tree because the beans from it are used to make flour. They also were a symbol to early settlers.
Species #2

 Scientific Name: Spermophilus Lateralis
Scientific Name: Spermophilus LateralisCommon Name: Ground Squirrel
Family: Sciuridae
Ground Squirrels adjust antipredator behavior in complex ways to diversity the predators that eat them. They migrate to other habitats to adapt.Snakes are major squirrel predators. Ground squirrels can hurt shrubs, vines, and trees by chewing on them. They also eat many grasses, seeds, grains, and nuts. They eat more before the winter so that they can live through the time when food won't be easy to get.
Because ground squirrels eat plants they are Herbivores.
Ground squirrel's are not domesticated and I feel they are co-evolving with humans by cleaning up crumbs and uneaten foods that humans leave behind.
Species #1

 Scientific Name: Zeamays
Scientific Name: ZeamaysCommon Name: Corn
Family: Poaceae
Corn is used in many food that we eat. There are economic benefits of improved soil quality with soil rotation (changing from one crop to a different crop after harvest) therefore you get higher yields.
Ethanol is produced from corn as a biomass through industrial fermentation, chemical processing and distillation. Ethanol is used as an alternative gasoline and petroleum. Greenhouse gas is released during ethanol production but is recaptured as a nutrient to the crops that are used in production.
I believe that corn is a domesticated species because corn is all around us in so many food that we eat.
Unit 4 Ethical Issue: Is Population the Problem? And Who Should Reproduce?
The article from Moses and Brown discussed many issues that relate to developed and under developed countries and what has an effect on population. Under developed nations have more children but don't use a lot of energy resources. Developed countries have fewer children but use more resources then under developed nations. One of the reasons for us using so many more resources is because we are using those resources to feed and help out under developed countries. Also we have many advantages that under developed countries do not have the options to and these were not mentioned in the article and can have an affect on population. In developed countries both the mother and father have careers therefore don't have the time to have more children. They also have the options to many different birth control contraceptives that allow them to prevent unwanted births.
Like the article, I believe that education in the developed countries has a lot to do with controlling population. So I really don't believe in the developed countries that population is a problem and does not need to be controlled like under developed countries.
Like the article, I believe that education in the developed countries has a lot to do with controlling population. So I really don't believe in the developed countries that population is a problem and does not need to be controlled like under developed countries.
Wednesday, July 23, 2008
Unit 4 Online Lab
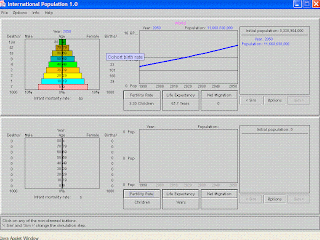
There are many countries that have a high fertility rate. The one I picked was the Soviet Union and it has a fertility rate of 2.29
2. What was your low fertility rate country and what was its fertility rate? The country that I selected for low fertility rate was Iraq and has a fertility rate of 7.00
3. Explain why high fertility rate results in a high percentage of young people in the population. How does this affect future population growth? I think that high fertility rates happen to younger people is because of unplanned pregnance.
4. Explain why low fertility rate leads to lots of middleaged people. I think that low fertility rates result in middleaged people because they have already started a family or have a good career and dont have time to have a baby.
5. Write ten adjectives or descriptive phrases for what you might expect life, people's attitudes, conditions on the streets, etc. will be like in each of those situations. Imagine a situation with lots of middle aged and older people in the population and write ten quick brain storm descriptors that you think it would be like. Then do the same for a situation with lots of children in the population.
Very few elementary schools and high schools, wouldnt need jobs working with children, putting time into other activities such as golfing, fishing, ect..., wouldnt be a lot of toys in the stores to buy, music would be different, television would change, video game sales would decline, fashion, electronics, and housing.
A lot of schools, would need a lot of jobs that deal with children, food, toys, the music would be for younger children, sports, out door activities, fashion, and bigger houses,
Compendium Review Chapters 22, 23 & 24


 Chapter 22
Chapter 22Evolution is a scientific theory, ideas that scientists have found to be all encompassing because they are based on evidence collected.
Evolution begins with the origin of life. Biology states that all living things are made of cells and every cell comes from a preexisting cell. Non living chemicals could be how the first cells came to be created by a chemical evolution.
Earth was probably formed over a 10 billion year period. Earth’s atmosphere is much different today then when it was first formed. The primitive atmosphere was more than likely formed by gases escaping from volcanoes so therefore had little if any free oxygen.
The oceans of the world were produced by enormous amounts of rain over hundreds of millions of years.
A protocell which can not reproduce but can carry on metabolism could have come into existence. Since it could not take in molecules in the ocean for food, it more than likely was an organism that took in preformed food and being a fermenter and not requiring free oxygen because primitive Earth had no free oxygen.
Scientists were trying to figure out how cells had both RNA and DNA. By doing many hypotheses they found out that RNA formed from enzymes and then they could use RNA as a template to form DNA.
In today’s cells, DNA replicates before cell division occurs because true cells reproduce. The replication process is carried out by enzymatic proteins.
The first true cells were the simplest of life forms and lacked a nucleus, later cells which have a nuclei evolved. All of these organisms are alive today.
Almost all living organisms use the same basic biochemical molecules, including DNA, ATP, and many enzymes. Humans share a large number of genes with much simpler organisms. Life’s vast diversity came about by only a slight difference in the regulation of genes.
Biological evolution: is the process by which a species changes through time.
Two aspects to this type of evolution: descent from a common ancestor and adapt to the environment and adapt to different environments and be able to survive and reproduce in this environment.
A mechanism for adaptation called natural selection. Members of a species vary in physical characteristics. There are limited resources that mean there is competition for it which results in unequal reproduction among members of a population.
Adaptation to changes in the environment and selects for better adapted traits natural section accounts for the great diversity life. Every organism adapt differently to their own way of life.
Fossils which are the actual remains of species that lived on Earth at least 10,000 to billions of years ago are the best evidence for evolution.
Fossils can be: trails, footprints, burrows, worm casts, preserved droppings, pieces of bones, impressions of plants, insects in tree amber, Most fossils are found embedded in rock. Many things have been learned about primitive life by studying fossils including history of life, climates and environments.
The origin of mammals is well documented by studying fossils. The earliest true mammals are about 200 million years old.
The study of distribution of plants and animals in different places throughout the world is Biogeography. There are different mix of plants and animals in separate continents, islands and seas. Some animal types may not be in some continents because they evolved somewhere else and had no way of reaching other parts even though the environment might be suited for them. Many unique species make their home in the islands of the world but are not found anywhere else in the world. The reason for this is they migrated to that island and then evolved into different species on that island. Many times evolution is influenced by the mix of plants and animals in a particular continent.
The anatomical similarities among organisms can be explained that the basic plan belonged to a common ancestor and the plan was adapted as each group continued along its own evolutionary path. Some are similar because they are inherited from a common ancestor, however in contrast some have structures that serve the same function but they are not constructed the same nor do they share a common ancestry.
During adaptation a species becomes suited to its environment, this process is natural selection. Variation, competition for limited resources such as food and adaptation are the elements of this process. This accounts for the diversity of life in the different environments and why the adaptations are varied.
Humans are primates, meaning they have mobile limbs, grasping hands, a flattened face, binocular vision, a large complex brain and a reduced reproductive rate. Humans are most closely related to monkeys and apes because monkeys and apes have certain characteristics similar to us.
The first modern humans were Neandertals and Cro-Magnons and later Homo habilis which may be the ancestor to modern human, the study of fossils date the early homo between 2.0 and 1.9 MYA and the jaw and teeth resemble those of humans. It is very unlikely that human evolution produced the same result in different places. Therefore human populations have evolved separately for along time with genetic differences.
Since the beginning of human evolution just like with other species, human beings have been widely distributed about the globe. Today we say that people have different ethnicities. One hypothesized theory is that human variations evolved to adapt to a certain environment, like the difference between humans skin color. However other differences among ethnic groups such as hair texture and shape of lips cannot be explained as adaptation to the environment. These features may have been fixed in different ethnic populations simply by genetics.
Chapter 23
Ecosystem: is a place where organisms interact with themselves and the environment physically and chemically.
Organisms are found on planet earth from the atmosphere to the depths of the oceans and everything in between is known as the biosphere. The entire biosphere is one giant ecosystem.
The different ecosystems
Temperature and rainfall define the biomes, which contain communities of organisms adapted to the regional climate
Tropical rain forest, which occurs at the equator, is dominated by large evergreen, broad leaved trees.
Savanna is tropical grassland that supports many types of grazing animals.
Temperate grasslands receive less rainfall than temperate forest and more water than deserts which lack trees.
Taiga is a very cold northern coniferous forest and the tundra which borders the North Pole, is also very cold, long winters and short growing seasons.
Aquatic ecosystems are those composed of freshwater and those composed of salt water.
The role of an organism in an ecosystem like how it gets its food, what it eats and how it interacts with other populations in the same community is a niche.
Non living components of the ecosystem are abiotic components. Biotic components are living things that are categorized by their food source.
Some species are autotrophs and are called producers because they produce food. Other species are called heterotrophs and they need a source of organic nutrients. They consume food so are therefore consumers.
Herbivores: animals that graze directly on plants or algae
Carnivores: animals that feed on other animals
Omnivores: animals that feed both on plants and animals
Detritus feeders: organisms that feed on detritus (decomposing particles of organic matter)
All species play an important role in the food chain, therefore are important to the ecosystem.
Global biogeochemical cycles: pathways by which chemicals circulate through ecosystems involve both living and nonliving components. All organisms require a variety of organic and/or inorganic nutrients. Global biogeochemical cycle can be gaseous or sedimentary.
The water cycle—evaporation from the ocean, precipitation to ocean, precipitation over land, transportation from plants, evaporation from soil, freshwater runoff, aquifer
The carbon cycle---plants take up carbon dioxide from the air and incorporate carbon into nutrients, when organisms respire carbon is returned to the atmosphere therefore carbon recycles to plants by the atmosphere, carbon dioxide from the air combines with water to produce HCO3, the amount of HCO3 in the water is in equilibrium with the amount of carbon dioxide in the air, living and dead organisms contain organic carbon and serve as reservoirs for the carbon cycle, plant and animal remains were transformed into fossil fuels, carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere.
Greenhouse gases are contributing significantly to an overall rise in the Earth’s ambient temperature, a phenomenon referred to by scientists as global warming. This effect could bring about other changes.
Chapter 24
Growth rate is determined by considering the different between the number of persons born per year and the number who die per year.
The carrying capacity is the maximum population that the environment can support for an indefinite period.
The more development countries (MDC) typified by countries in north America and Europe, population growth is modest and people enjoy a good standard of living.
The less development countries (LDCS) typified by some countries in Asia, Africa, and Latin America population growth is dramatic and the majority of people live in poverty.
People can help out ecological by driving energy efficient car, living in a smaller house, owning fewer possessions, eating vegetables as opposed to meat.
Living right on the coast can be bad because it leads to beach erosion and loss of habitat for marine organisms and loss of a buffer zone for storms. About 70% of the world’s beaches are eroding.
In water poor areas of the world, people might not have clean drinking water or impure. Food comes from three activities: growing crops, raised animals and fishing the seas.
Genetic engineering produces transgenic plants with new and different traits. Researchers hope to produce crops that tolerate salt drought and cold.
Modern society runs on various types of energy. Some are nonrenewable such as fossil fuels and global climate change. Others are renewable: hydropower,geothermal energy, wind power, energy and the solar hydrogen revolution and photovoltaic solar cell.
Life on earth is biodiversity which means the number of species on earth. We are now in a biodiversity eristic because of extinction. Why is biodiversity so important? Different species perform useful services for human beings and contribute greatly to the value we should place on biodiversity.
A sustainable society will always be able to provide the same amount of goods and services for future generations as it does at present.
We are quick to realize that population growth in the LDCs creates an environmental burden, we also need to consider excessive resource consumption of the MDCs also stresses the environment.
Compendium Review Chapters 16 & 17


Chapter 16
Puberty is events that a child goes through in order to become sexually competent young adults it happens between the ages of 11 & 13 in girls and 14 & 16 in boys. Until puberty is complete, the reproductive system does not begin to fully function and at this time the individual is capable of producing children.
Reproduction organs have these functions:
In men they produce sperm within testes, and in females they produce eggs within ovaries.
Males nurture and transport sperm in ducts till it leaves the penis and in females they transport eggs in uterine tubes to the uterus.
The penis delivers sperm to the vagina that receives the sperm. The vagina also is the exit for menstrual flow and is the birth canal.
The uterus allows the fertilized egg to develop in her body. After the birth the female breast provides milk.
The testes and ovaries produce sex hormones that help maintain the testes and ovaries and have effects on the body. In the females the sex hormones allow pregnancy to continue.
Male Reproductive Organs and their function:
There are two testes and they are suspended in the sacs of the scrotum and they produce sperm and sex hormones. Sperm matures in a tightly coiled duct lying outside each testis. Mature sperm is required for it to swim to the egg.
These tightly coiled ducts where sperm matures are called epididymides.
Vasa deferentia is another storage place for sperm after leaving the epididymides. Each Vas deferens passes into the abdominal cavity where it curves around the bladder and empties into the ejaculatory duct.
Urethra is where the ejaculatory ducts enter and it conducts sperm. The urethra carries either urine or semen at different times.
Seminal vesicles, Bulbourethral glands and prostrate gland each contribute fluid to the semen. The seminal vesicles also add nutrients.
Penis is an organ of sexual intercourse. During sexual arousal nerves release nitric oxide, and this stimulus leads to the production of cyclic guanosine monophosphate which causes the smooth muscle of the arterial walls to relax. The erectile tissue will fill with blood and the veins that take blood away from the penis are compressed and the penis becomes erect. Ejaculation occurs as sexual stimulation intensifies, sperm enters the urethra from each vas deferens and the glands contribute secretions to the seminal fluid. Rhythmic muscle contractions cause it to be expelled from the penis in spurts. At the time of ejaculation, sperm leaves the penis in a fluid called semen.
The penis is covered by a layer of skin called foreskin. Shortley after birth this skin is surgical removed.
The prostrate can become enlarged in older men which squeezes off the urethra making urination painful and difficult. This condition can be treated medically.
Erectile dysfunction or impotency occurs when the erectile tissue does not expand enough to compress the veins. Medications can treat Erectile dysfunction by inhibiting the enzyme that breaks down cyclic guanosine monophosphate making it possible for a full erection.
Condoms are 97% effective in preventing pregnancy if they are used right. The reason is because a condom catches seminal fluid because it is placed over the erect penis so that it does not enter the vagina.
Mature sperm contain a head, middle piece and a tail. Mitochondria are in the middle piece that provides energy for the movement of the tail. The head has a nucleus covered by a cap which stores enzymes needed to penetrate the egg. Flagellated sperm is very small compared to the egg. As it swims to the egg it is specialized to carry only chromosomes and the egg is specialized to wait for the arrival of the sperm.
Testosterone is the main sex hormone in males. It is essential for the normal development and function of the male reproductive organs. It also brings about male sex characteristics and development of muscles. Males development of hair on face, chest and other regions such as their back is due to testosterone.
Female Reproductive Organs and their function:
Oviducts also called uterine or fallopian tubes and they extend from the uterus to the ovaries. They are not attached to the ovaries but they have finger like projections that sweep over the ovaries. An egg bursts from an ovary during ovulation into an oviduct and this is where fertilization occurs. Zygote formation which is the first cell of a new human being takes place in these oviducts.
Uterus is where the developing embryo arrives after several days. The uterus is referred to as the womb because it houses the embryo and this is where development of the embryo and fetus takes place. The uterus is a muscular organ about the size and shape of an inverted pear. Endometrium is the lining of the uterus which participates in the formation of the placenta. The placenta supplies nutrients needed for fetal development.
Ovaries, there are two and they produce eggs and sex hormones. An ovary contains follicles and each one contains an oocyte which is an immature egg. Only a small number of follicles ever mature because a female usually produces only one egg per month during the ovarian cycle.
Cervix is at the lower end of the uterus and contains the opening to the uterus and it enters the vagina nearly at a right angle. A small opening in the cervix leads to the vaginal canal.
Vagina is a tube that lies to the small of the back. The vagina serves as the birth canal and receives the penis during sexual intercourse. It also is the exit for menstrual flow.
The urinary and reproductive systems in a female are entirely separate unlike a male. The urethra carries only urine whereas the vagina serves as the birth canal and organ to receive the penis during intercourse.
A pap test is very important for early detection of cancer in the cervix. The pap test is done by removing cells from the region of the cervix and examining them under a microscope. If the cells from the pap are cancerous they may recommend that you have a hysterectomy. A hysterectomy is the removal of the uterus including the cervix. A radical hysterectomy is removal of the ovaries as well.
The clitoris is the organ of sexual arousal in a female and can swell to two or three times it usual size because it becomes engorged with blood during sexual stimulation. The thrusting of the penis and the pressure of the pubic symphyses of the partners’ act to stimulate the clitoris.
Estrogen and Progesterone are hormones that affect not only the uterus but other parts of the body too. Estrogen is responsible for the secondary sex characteristics in females like body hair and fat distribution. Both hormones are required for breast development.
If an egg is not fertilized by a sperm cell than it dies shortly after be released from the ovary. When appropriate the vesicular follicle bursts releasing the egg surrounded by a clear membrane which is ovulation.
Menopause occurs in a women’s life between the ages of 45 and 55 and this is when the ovarian cycle ceases. The ovaries are no longer responsive to the gonadotropic hormones and the ovaries no longer secrete estrogen and progesterone. At the onset menstruation becomes irregular. However it is still possible for a woman to conceive as long as it occurs. Menopause is not considered complete until menstruation is absent for a year.
The different forms of contraceptives (birth control) are the intrauterine device, hormone skin patch, Depo-Provera, diaphragms and spermicidal jelly, female condom, male condom, implant and oral contraception. Natural family planning which is keeping records to determine day of ovulation. Pregnancy can’t occur when the female is not ovulating. Each one has a different effectiveness and has different side affect on different people. Abstinence (not engaging in sexual intercourse) is the most reliable form of birth control.
Tubal ligation consists of cutting and sealing the oviducts on a female, pregnancy rarely occurs because passage of the egg through the oviducts has been blocked.
Vasectomy consists of cutting and sealing the vas deferens on both sides on a male so sperm can not reach the seminal fluid that is ejected at the time of orgasm.
Both tubal ligation and vasectomy are methods that bring about sterilization and are permanent.
Infertility is the failure of a couple to achieve pregnancy after one year of regular unprotected intercourse. There are several causes of infertility in males and females. The most common cause in males is low sperm count. The most significant factor in females is body weight.
The different types of sexually transmitted diseases (STD’S):
STD’S CAUSED BY VIRUSES:
Genital warts carriers might not have any signs. When present the warts are mostly found on the penis and foreskin of men and near the vaginal opening in women.
Genital herpes type 1 usually cause cold sores and fever blisters
Type 2 more often causes genital herpes
HIV/AIDS- AIDS is acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. HIV infects and destroys cells of the immune system. Aids is the advanced stage of HIV when a person develops one or more infections due to the immune system being severely weakened.
Hepatitis infects the liver and can lead to liver failure.
STD”S CAUSED BY BACTERIA:
Chlamydia symptoms are in men are mild burning sensation during urination and vaginal as well as symptoms of a urinary tract infection.
Gonorrhea symptoms are pain during urination and a thick greenish yellow urethral discharge in men. Gonorrhea can spread to internal parts of the body causing heart damage or arthritis.
Syphilis has three stages. #1- sore with hard edges which indicates the site of infection #2- break out in a rash that does not itch #3- this stage last until the person dies and may affect cardiovascular system by causing aneurysms. The disease may affect the nervous system resulting in psychological disturbances. Large ulcers may develop on the skin or within internal organs.
Chapter 17
Fertilization is the joining of sperm and egg to form a zygote the first cell of the new individual then it goes over the process the sperm cell goes through to fertilize an egg.
Pre Embryonic and embryonic development
Process of development
Cleavage happens right after fertilization then the zygote divides first into 2 then 4,8,16 and 32 cells. Cell division during this stage is mitotic and each cell will receive a full complement of chromosomes and genes.
Growth during the embryonic development cell division happens by an increase size of the daughter cells.
Morphogenesis is the shaping of the embryo and is shown when certain cells are seen to move or migrate in relation to other cells. By each one of these movements the embryo begins taking shape.
Differentiation when cells form a specific structure and function, differentiation occurs. The first system that becomes visible is the nervous system.
Stages of development
The first week of pre embryonic development happens during this time.
Second week the embryo usually begins the process of implanting itself in the wall of the uterus.
Third week two important organ systems are formed and start appearing. The organs are the nervous system and development of the heart begins.
Fourth and Fifth weeks the embryo is barely larger then the height of this print.
Sixth through eighth week the embryo changes to a form that is easily recognized as a human being.
The normal gestation period is 280 days, however only about 5% of babies actually arrive on the predicted date. A doctor can calculate the due date by adding 280 days to the start of the womans last menstruation date.
Pregnancy and birth
When first pregnant the women might experience nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, and fatigue. Although some women say that during this time they have increase in energy. Also during pregnancy the mother gains weight due to breast and uterine enlargement weight of the fetus, amount of amniotic fluid, size of the placenta, her own increase in total body fluid and an increase in storage of proteins, fats and minerals. The increase in weight can result in lower back problems. The uterus relaxes, the pulmonary values increase there can be other problems as the uterus enlarges.
Birth
At first the uterus has light contractions but near the end of pregnancy the contractions may become stronger and more frequent. The uterine contractions are induced by a stretching of the cervix that also brings the release of oxytocin from the posterior pituitary gland. Prior to the first stage of parturition which is the process of giving birth to an offspring there can be a bloody show caused by expulsion of a mucous plug from the cervical canal.
Stage 1
The cervical canal slowly disappears as the lower part of the uterus is pulled upward towards the baby’s head. The baby’s head then acts as a wedge to assist cervical dilation.
Stage 2
The uterine contractions occur every 1-2 min and last about 1 min. They are followed by the desire to push and bear down. As the baby’s head is into the vagina the desire to push increases. When the head get to the exterior it turns so the back of the head is uppermost. As soon as the head is out, the doctor may hold the head and guide it downward while one shoulder and then the other emerges. Once the baby’s breathing is normal the umbilical cord is cut and tied severing the child from the placenta.
Stage 3
The placenta or afterbirth is delivered during the third stage of parturition. 15 minutes after delivery the uterine muscular contraction shrink the uterus and dislodge the placenta. The placenta then is expelled into the vagina.
Development does not cease once birth has occurred. It continues through the stages of life. Infancy, childhood, adolescence and adulthood. Aging contributes to progressive changes that contribute to an increased risk of infirmity, disease and death. Research indicates that aging has a genetic basis.
Embronic and Fetal Development Online Lab








Two months: A this point the baby is about the size of a kidney bean and is constantly moving. The baby now has slightly webbed fingers.
Three months: The baby is about 3 inches long and weighs about an ounce and the fingerprints are now showing.
Four months: The baby is about 5 inches long and weighs about 5 ounces. The skelton is starting to get hard and changing from rubbery cartilage to bone.
Five months: The baby is about 10 inches long if you streach out its feet also by now the eyebrows and eyelids are showing.
Six months: The baby now weighs about a pound and half and the wrinkled skin is starting to become smooth and is putting on baby fat.
Seven months: The baby is 3 pounds and is about 15 inches long. The baby can also now open their eyes and follow light.
Eight months: The baby weighs 4 3/4 it becomes rounder and its lungs are well developed.
Nine months: At this point the baby weighs about 7 pounds and is more then 19 inches but these numbers can be different in every baby.
Friday, July 11, 2008
Thursday, July 10, 2008
Unit 3 Lab Project: Build A Moveable Limb
Introduction: This is a model of a moveable elbow built out of construction paper and metal brads that connected the bicep to the anterior band. The parts that are found in the model are bones, tendons, and muscles. Each one of these allow it to bend and contract.
Conclusion: By building a model I have learned about how bones, tendons and muscles allow our bodies to move a certain way. In certain different parts of the body bones, muscles and tendons can aid in supporting and protecting our bodies. The elbow works simular to a hinge because it bends and straightens. All the nerves that travel down the arm pass through the elbow and these nerves carry signals from the brain to the muscles and this makes the arm move. The elbow is what provides stability as we position our forarm to use our hand.
Conclusion: By building a model I have learned about how bones, tendons and muscles allow our bodies to move a certain way. In certain different parts of the body bones, muscles and tendons can aid in supporting and protecting our bodies. The elbow works simular to a hinge because it bends and straightens. All the nerves that travel down the arm pass through the elbow and these nerves carry signals from the brain to the muscles and this makes the arm move. The elbow is what provides stability as we position our forarm to use our hand.
Online lab: leeches


Why use leeches in neurophysiology experiments? They are relatively small in number and have a large size of neurons.
What is the difference between a sensory and a motor neuron? A sensory neuron is a nerve cell that transmits nerve impulses to the cns after a sensory receptor has been stimulated. A motor neuron conducts impulses away from the cns and innervates effectors.
Do you think a leech experiences pain? What is pain? No they do not feel pain because they do not have the necessary brain systems that vertebrates have in order to process pain.
What were the two most interesting things about doing this lab? Just learning about neurophysiology in all because i had never learned anything about them before.
Anything you found confusing or didnt like about the lab? Just trying to figure out the lab at first was a little confusing.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)










