Saturday, June 28, 2008
Self and Unit Evaluation
REGARDING YOUR OWN PERFORMANCE
What were the three aspects of the assignments I've submitted that I am most proud of? The three assignments that I’m most proud of are the compendium reviews and the ethical issue.
What two aspects of my submitted assignments do I believe could have used some improvement? The two aspects that I feel could have used a lot more time would be the lab project and the online blood pressure lab.
What do I believe my overall grade should be for this unit? My overall grade for this unit should be a low B. I feel like I have worked hard on each assignment and have done it to the best of my ability.
How could I perform better in the next unit? To help me do better next time, I should get more of the unit covered in the first week. I was really sick with the flu for a week and couldn't hardly get out of bed so was hard to do my assignments.
REGARDING THE UNIT
At what moment during this unit did you feel most engaged with the course? The moment that I felt most engaged in the unit was when I was doing the lab even though I’m not sure if the results are right.
At what moment unit did you feel most distanced from the course? During the online blood pressure lab because I wasn’t too sure what all I had to do. I also couldn’t get the table and graph emailed to myself.
What action that anyone (teacher or student) took during this unit that find most affirming and helpful?
What action that anyone (teacher or student) took during this unit did you find most puzzling or confusing? Sometimes it is nice to be in a classroom instead of online trying to figure out everything on your own. Not knowing if you are actually doing it right.
What about this unit surprised you the most? The most surprising thing about this unit was learning about the different places your heart pumps blood to and just how important that is to us.
What were the three aspects of the assignments I've submitted that I am most proud of? The three assignments that I’m most proud of are the compendium reviews and the ethical issue.
What two aspects of my submitted assignments do I believe could have used some improvement? The two aspects that I feel could have used a lot more time would be the lab project and the online blood pressure lab.
What do I believe my overall grade should be for this unit? My overall grade for this unit should be a low B. I feel like I have worked hard on each assignment and have done it to the best of my ability.
How could I perform better in the next unit? To help me do better next time, I should get more of the unit covered in the first week. I was really sick with the flu for a week and couldn't hardly get out of bed so was hard to do my assignments.
REGARDING THE UNIT
At what moment during this unit did you feel most engaged with the course? The moment that I felt most engaged in the unit was when I was doing the lab even though I’m not sure if the results are right.
At what moment unit did you feel most distanced from the course? During the online blood pressure lab because I wasn’t too sure what all I had to do. I also couldn’t get the table and graph emailed to myself.
What action that anyone (teacher or student) took during this unit that find most affirming and helpful?
What action that anyone (teacher or student) took during this unit did you find most puzzling or confusing? Sometimes it is nice to be in a classroom instead of online trying to figure out everything on your own. Not knowing if you are actually doing it right.
What about this unit surprised you the most? The most surprising thing about this unit was learning about the different places your heart pumps blood to and just how important that is to us.
Friday, June 27, 2008
Exercise Physiology
Unit 2 lab project
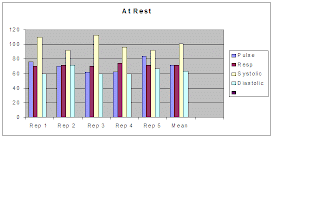
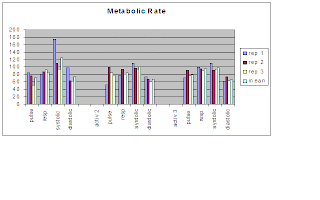
Introduction: Measured my pulse, respiration rate, and blood pressure at rest and then after doing certain activities that I picked out. Before getting started I measured all of these before I even started doing my activities. In order to measure each one of these I used an electronic blood pressure cuff that gave me the systolic, diastolic and then the pulse. To find the respiration rate I counted the number of respirations in half a minute and then multiplied by two.
Hypothesis: Before even starting this experiment I thought that all my metabolic measurements would greatly increase especially doing jumping jacks and walking.
Analysis of data: From each activity the pulse, respiration, and blood pressure slightly went up in most cases. However I thought the data would have increased a lot more then they did. As I took my respiration rate after the activities the beat was stronger and it was a lot easier for me to count.
Problems with your data or technique: Because the levels didnt go up as much as I thought they would. I thought something was wrong with the electronic blood pressure cuff so I redid some of the activities and redid the readings but nothing changed.
Conclusion: The harder an activity that you do the harder your body has to work to keep your blood pumping and helps keep your body temperature stable. Therefore as long as the circulatory system is working correctly it keeps the metabolic parameters stable even when doing exercise.
Introduction: Measured my pulse, respiration rate, and blood pressure at rest and then after doing certain activities that I picked out. Before getting started I measured all of these before I even started doing my activities. In order to measure each one of these I used an electronic blood pressure cuff that gave me the systolic, diastolic and then the pulse. To find the respiration rate I counted the number of respirations in half a minute and then multiplied by two.
Hypothesis: Before even starting this experiment I thought that all my metabolic measurements would greatly increase especially doing jumping jacks and walking.
Analysis of data: From each activity the pulse, respiration, and blood pressure slightly went up in most cases. However I thought the data would have increased a lot more then they did. As I took my respiration rate after the activities the beat was stronger and it was a lot easier for me to count.
Problems with your data or technique: Because the levels didnt go up as much as I thought they would. I thought something was wrong with the electronic blood pressure cuff so I redid some of the activities and redid the readings but nothing changed.
Conclusion: The harder an activity that you do the harder your body has to work to keep your blood pumping and helps keep your body temperature stable. Therefore as long as the circulatory system is working correctly it keeps the metabolic parameters stable even when doing exercise.
Ethical Issue 2

We start eating at a very young age and depend on our parents to feed us the things that will help us grow and mature. But as we get older we get to decide what we want to put into our mouths. I believe that picking the foods that we pick is mainly a result of our culture. For instance in my house every meal that we have has a main course of meat and mostly beef. The sides are normally some kind of vegetable like corn, green beans, and the other side is potatoes, rice or something kind of like that. The reason that my parents are used to eating these foods is their parents fed them the same kind of foods. Both of my parents grew up on the farm so they were raised eating meats and corn. They raised and butchered their own beef and the vegetables were grown in their garden.
As we have noticed with having so many cultures in the United States it has brought many different kind of foods with it. So by living in the US we have been able to experience and try many different types of foods that we might not have had a chance other wise. Where I live I’m able to eat different types of foods like Mexican, Native American, and Chinese. I also have seen many different practices out there for the different types of food. So I feel that the food that we put in our mouth from day to day has a big part of what type of culture we are from.
As we have noticed with having so many cultures in the United States it has brought many different kind of foods with it. So by living in the US we have been able to experience and try many different types of foods that we might not have had a chance other wise. Where I live I’m able to eat different types of foods like Mexican, Native American, and Chinese. I also have seen many different practices out there for the different types of food. So I feel that the food that we put in our mouth from day to day has a big part of what type of culture we are from.
Blood Pressure Lab


The blood pressure test ranged from females age 11-54 and males 11-54. You would pick which age group you wanted to choose from and then you would cheek there blood pressure. There were a couple things that were listed on there chart as the reason they had high blood pressure. The reason we lack of exercise, family history of hypertension, high salt diet and alcohol consumption. The higher in age we got it was mostly high due to the lack in exercise. So what is blood pressure exactly? Blood pressure refers to the force by circulating blood on the walls of blood vessels and constitutes one of the principal vital signs. The pressure decreases as blood moves through arteries, arteries, arterioles, capillaries and veins. Blood pressure usually is about arterial pressure which is pressure in the large arteries, and arteries. This is the blood that takes the blood away from the heart
Pulse: In this lab we also learned how to take a pulse. In order to take a pulse this is what you have to do. The artery on the thumb side of the wrist. Touch this area lightly until you feel your pulse or heart beat. Count the amount of heart beats for 15 seconds and multiply by four this will give you your daily pulse rate. This pulse is different from everybody is only the indicator of your resting plus rate. Normal for me 72 beats per min. For women 80 beats per min either side of those rates fall into the normal range
Compendium Review Chapter 8

 The gastrointestinal tract is where all the tubes are located for the organs of the digestive system. Some molecules are too big so they can’t get across the plasma membrane. The purpose is to break down these macromolecules to their unit molecules. Mainly sugars, amino acids, fatty acids and glycerol, can cross plasma membranes. Our food also has water salts, vitamins, and minerals that helps our body function normally.
The gastrointestinal tract is where all the tubes are located for the organs of the digestive system. Some molecules are too big so they can’t get across the plasma membrane. The purpose is to break down these macromolecules to their unit molecules. Mainly sugars, amino acids, fatty acids and glycerol, can cross plasma membranes. Our food also has water salts, vitamins, and minerals that helps our body function normally.These functions are necessary to our digestive process:
Ingestion: happens when the growth lets food in and can have something to do with our diet. That’s why learning good nutrition is highly important.
Digestive: mechanical or chemical mechanical is when food is divided into pieces that might be used by the digestion enzymes. Chewing our food good before swallowing it helps with digestion. A chemical process begins in the mouth and isn’t complete until food reaches the small intestine.
Absorption: when unit molecules are produced by digestion and cross the wall of the GI tract then enter the cells that are lining the tract. After that the nutrients enter the blood to be delivered to the cells.
Elimination: molecules that can’t be digested have to be eliminated. It is removed from the anus in the form of feces which is defecation.
The four layers of the digestive tract
The four layers of the digestive tract
First layer of the wall is called the mucosa also known as the mucous membrane. It produces mucus which protects the walls from the digestive enzymes. In the mouth, stomach and small intestine mucosa has glands that secrete or receive digestive enzymes.. Divertulosis is a portion of mucous that has pushed through and formed layers so pouches can be created.
Second layer the GI wall is called the sub mucosa. This layer contains loose connective tissue that contains blood vessels, lymphatic vessel, and nerves. All these vessels will carry the nutrients that were absorbed by the mucosa.
Third layer is the muscular which contains two layers of smooth muscle. Inner layer encircles the tract. The outer layer lies in the same way as the tract. When these muscles contract it accounts for movements of digestion of food from the esophagus to the anus.
Fourth layer of the tract is serosa. The secrete contains a serous fluid that is a part of the peritoneum, which is the inner lining of the abdominal cavity.
First part of digestive tract
The first couple parts of the digestive tract are the mouth, pharynx, and the esophagus.
The first couple parts of the digestive tract are the mouth, pharynx, and the esophagus.
Mouth: Mechanical digestion occurs when the teeth chew food into little pieces in order to swallow them. The first two years of life we have 20 smaller teeth also known as our baby teeth. Then we eventually get 32 adult teeth. In addition to the 32 teeth you also might gain a third pair of molars or also called wisdom teeth. These don’t always come through so then they might have to be removed. Each tooth has two main divisions a crown and a root.
Crown: layer of enamel with a hard outer covering of calcium, dentin a thick layer of bone like material, an inner pulp that contains nerves and blood vessels.
Root: dentin and pulp found in the root.
The pharynx and the esophagus
Mouth and nasal passages lead to a cavity which is the pharynx. Food passage and air passage cross the pharynx because the trachea is an anterior to the esophagus.
The pharynx and the esophagus
Mouth and nasal passages lead to a cavity which is the pharynx. Food passage and air passage cross the pharynx because the trachea is an anterior to the esophagus.
Esophagus: a long narrow tube that takes our food to the stomach.
The stomach and small intestine
The stomach and small intestine
The stomach: is a thick J shaped wall that is the left side beneath the diaphragm. The stomach stores food and.initiates the digestion of protein and controls the movement of chime into the small intestines. The stomach normally empties in 2-6 hours. When food leaves it is a think, soupy liquid which is called chime. That liquid then enters the small intestine in small amounts.
Small intestine: is small in diameter but big in length. It is about 18 feet long and contains enzymes to digest different types of foods. These foods are primarily carbohydrates, proteins and fats. The wall of the small intestine absorbs molecules namely sugars, amino acids, fatty acids and glycerol, that are products of the digestive process. Nutrients are absorbed into the vessels of a villus which contains blood capillaries and small lymphatic capillary. Vessels carry fluid to the cardiovascular system then sugars, amino acids enter blood capillaries of villus. Glycerol and fatty acids enter the epithelial cells of villus and with each cell are joined packaged as lipoprotein droplets called chylomicreins which enter a lacteal. After nutrients are absorbed they are the taken to the cells of the body by the bloodstream.
Three accessory organs and regulation of secretions
Three accessory organs and regulation of secretions
Pancreas: fish shaped spongy, grayish pink organ that goes across the back of the abdomen which is behind the stomach. It is also an endocrine gland that secretes the hormone in insulin into the blood. This works when blood glucose levels rise but the pancreas produces a lot of insulin so that the level comes down.
The liver is the largest major metabolic gland in our bodies and is mainly in the upper right sections of the abdominal cavity under the diaphragm. It contains about 100,000 lobuis that are structural and functional units. Liver is a storage unit and it removes iron and vitamins A,D,E,K and B 12 from the blood and stores theandm.
The liver is the largest major metabolic gland in our bodies and is mainly in the upper right sections of the abdominal cavity under the diaphragm. It contains about 100,000 lobuis that are structural and functional units. Liver is a storage unit and it removes iron and vitamins A,D,E,K and B 12 from the blood and stores theandm.
The liver produces glucose in order for food to get broken down.
The large intestine has the cecum, the colon, the rectum and the anal canal. Functions of the large intestine are to absorb water that is really valuable for use. It prevents the body from dehydration and absorbs vitamins that are produced by bacteria.
The large intestine has the cecum, the colon, the rectum and the anal canal. Functions of the large intestine are to absorb water that is really valuable for use. It prevents the body from dehydration and absorbs vitamins that are produced by bacteria.
Classes of nutrients
Carbohydrates: products such as refined grains
Proteins: vegetables, seeds and nuts also grains supply us with amino acids
Lipids: oils containing fatty acids
Corn and sunflower oil are high in polyunsaturated fatty acids
Carbohydrates: products such as refined grains
Proteins: vegetables, seeds and nuts also grains supply us with amino acids
Lipids: oils containing fatty acids
Corn and sunflower oil are high in polyunsaturated fatty acids
Compendium Review Chapters 5,6,7

 Chapter 5
Chapter 5Cardiovascular system
Consists of the heart that pumps the blood, and the blood vessels which help with the blood flow. With every beat of the heart blood is sent into the blood vessels and always contained within blood vessels. This helps because blood removes waste products from tissue fluid. In order for cells to continue there existence it has to bring tissue fluid, oxygen and nutrients
Consists of the heart that pumps the blood, and the blood vessels which help with the blood flow. With every beat of the heart blood is sent into the blood vessels and always contained within blood vessels. This helps because blood removes waste products from tissue fluid. In order for cells to continue there existence it has to bring tissue fluid, oxygen and nutrients
Lymphatic system: is assistant to cardiovascular because its vessels collect excess tissue fluid and then return it to the cardiovascular system.
The different kinds of blood vessels
The different kinds of blood vessels
The arteries: has three layers, inner most layer is a thin layer of cells which are called endothelium. Middle layer is relatively thick layer of smooth muscle and elastic tissue and the outer layer is connective tissue. The walls of the artery gives support when blood enters under pressure. The elastic tissue helps an artery to expand to absorb the pressure.
The capillaries: Arterioles branch into capillaries. Capillary is an extremely narrow microscopic tube with a wall made of only endothelium with a basement membrane. Total surface area in humans is about 6,300 square meters of capillaries as they are in every part of the body.
The veins: venules are small veins that drain blood from capillaries and then join to form a vein. Have the same three layers as arteries but less smooth muscle in the middle layer and less connective tissue in the outer layer of veins. The outer layer allows blood to flow only towards the heart when open and prevents its blood from going back when closed.
The heart is cone shaped muscular organ. To get the approximate size of the heart make a fist then clasp the fist with your opposite hand. A cardiac cycle is each heart beat. The heart contrasts or beats about 70 times a minute and each beat lasts about .85 seconds. Normal adult rate at rest can vary from 60 to 80 beats per minute. The lub sound happens when increasing pressure of blood inside ventricle forces the cusps of the AV value to slam shut. The dup sound happens when the ventricles relax and blood in the arteries pushes back, causing the semi lunar value to close.
Pulse normally indicates the heart rate. The pulse rate is usually 70 beats per minute but can vary between 60 and 80 beats per minute.
Blood pressure: pressure of blood against the wall of the blood vessel. A sphygmonanometer is used to measure blood pressure. Normal resting blood pressure for a young adult is said to be 120 mm mercury over 30
Chapter 6 Blood
Human bodies contain about 5 liters of blood. Three categories blood fall into: transport, defense and regulation. Blood delivers oxygen from the lungs and nutrients from digestive tract to the tissue when an exchange takes place. Blood defends the body against invasion by pathogens in many ways. Some blood cells are capable of phagocytizing and destroying pathogens others produce and secrete antibodies into blood. Blood regulatory functions help regulate our body temperature by picking up heat from muscles and transporting it to the body.
Human bodies contain about 5 liters of blood. Three categories blood fall into: transport, defense and regulation. Blood delivers oxygen from the lungs and nutrients from digestive tract to the tissue when an exchange takes place. Blood defends the body against invasion by pathogens in many ways. Some blood cells are capable of phagocytizing and destroying pathogens others produce and secrete antibodies into blood. Blood regulatory functions help regulate our body temperature by picking up heat from muscles and transporting it to the body.
Red blood cells are small biconcave aisles that lack a nucleus when mature. There are 4-6 million red blood cells per mm of the whole body.
White blood cells are different from red blood cells they are longer and have a nucleus. White blood cells lack hemoglobin and are translucent unless stained. Only 5,000-11,000 per mm of blood. White blood cells fight infection and are a big part to the immune system. Two types of white blood cells: granular leukocytes and agranular leukocytes.
Chapter 7
Bacteria: single cell prokaryotes and they don’t have a nucleus. The three different shapes of bacteria anatomy are: bacillus has a rod shape; coccus has a spherical shape and a spirillum is curved. Bacteria have a cell wall that has unique amino disaccharide. Bacteria independent cells that metabolically competent and they reproduce by binary fission. The single chromosome attached to the plasma membrane is copied. Then as the cell gets bigger the chromosomes separate and the new formed plasma membrane and cell wall separate the cell into two cells.
Bacteria: single cell prokaryotes and they don’t have a nucleus. The three different shapes of bacteria anatomy are: bacillus has a rod shape; coccus has a spherical shape and a spirillum is curved. Bacteria have a cell wall that has unique amino disaccharide. Bacteria independent cells that metabolically competent and they reproduce by binary fission. The single chromosome attached to the plasma membrane is copied. Then as the cell gets bigger the chromosomes separate and the new formed plasma membrane and cell wall separate the cell into two cells.
Viruses: are the gap between the living and the nonliving. Outside a host viruses are mainly chemicals that store themselves. With the chance they will replicate inside cells and during this certain period they seem to be alive. Viruses are a cellular which means they aren’t composed of cells. A virus particle is about four times smaller then that of bacteria. Viruses always have two parts an outer capsid composed of protein and an inner core of nucleic acid.
The body puts up many barriers the entry to these barriers can be physical and chemical that serve as first line of defense against an infection.
Skin and mucous membrane, chemical barriers, resident bacteria.
The second line of defense is by the inflammatory response.
When all these have failed to prevent an infection we have specific defenses that can come into play. Which are either B cells or T cells.
Skin and mucous membrane, chemical barriers, resident bacteria.
The second line of defense is by the inflammatory response.
When all these have failed to prevent an infection we have specific defenses that can come into play. Which are either B cells or T cells.
The web activities deal with the different types of things from the chapters for instance phagocytosis, immunity, and HIV & AIDS. There were different types of videos and web sites for each one of the activities. By having videos and a different look from the book you can get a different look at things and gain more knowledge.
Friday, June 13, 2008
Self and Unit Evaluation
Regarding My Own Performance:
1. What were the three aspects of the assignments I've submitted that I am most proud of? The three aspects of the assignment that I’m most proud of are the making of the cell, and then posting all my pictures of the finished cell. The other two things that I’m also proud of are the online lab assignments and then adding my finish lab write ups and pictures into my blog.
2. What two aspects of my submitted assignments do I believe could have used some improvement? The two assignments that I could have used a little more time on would be the Compendium Review.
3. What do I believe my overall grade should be for this unit? I think I worked extremely hard on this unit and trying to figure out how to add all of it into a blog was really challenging for me. I stayed up many nights late to try and get all my assignments done and blogged. I feel that I should get a passing grade for my attempts at doing everything and hopefully finally getting everything blogged right. But all in all I’m very happy with the way things turned out and I have learned a great deal about cells and genetics.
4. How could I perform better in the next unit? Now that I have my book and won't have to wait for it, I plan on getting started a lot earlier so that I don’t have to rush and stress to get assignments done on the due date.
Regarding the Unit:
1. At what moment during this unit did you feel most engaged with the course? The time where I felt most engaged with the unit would have to be when I started building my working cell. It was very hands on so being able to see the parts of the cell in a different way just made me understand everything about a cell and how everything works just that much better.
2. At what moment did you feel most distanced from the course? I felt most distanced from the unit when I had to figure how to put all the work that I did into a blog. To be really honest the blogging part really stressed me out because I wasn’t sure if I was doing what I needed to do.
3. What action that anyone took during this unit did you find most affirming and helpful? When the teacher actually explained to me how I had to post all my assignments into the same blog that is when I finally understood what I was doing.
4. What action that anyone took during this unit did you find most puzzling or confusing? Just the whole blogging thing again but I have a better understanding of it now.
5. What about this unit surprised you the most? I think learning about the different genotypes and phenotypes, also learning about the genetic disorders. These were the most interesting parts of the unit for me.
1. What were the three aspects of the assignments I've submitted that I am most proud of? The three aspects of the assignment that I’m most proud of are the making of the cell, and then posting all my pictures of the finished cell. The other two things that I’m also proud of are the online lab assignments and then adding my finish lab write ups and pictures into my blog.
2. What two aspects of my submitted assignments do I believe could have used some improvement? The two assignments that I could have used a little more time on would be the Compendium Review.
3. What do I believe my overall grade should be for this unit? I think I worked extremely hard on this unit and trying to figure out how to add all of it into a blog was really challenging for me. I stayed up many nights late to try and get all my assignments done and blogged. I feel that I should get a passing grade for my attempts at doing everything and hopefully finally getting everything blogged right. But all in all I’m very happy with the way things turned out and I have learned a great deal about cells and genetics.
4. How could I perform better in the next unit? Now that I have my book and won't have to wait for it, I plan on getting started a lot earlier so that I don’t have to rush and stress to get assignments done on the due date.
Regarding the Unit:
1. At what moment during this unit did you feel most engaged with the course? The time where I felt most engaged with the unit would have to be when I started building my working cell. It was very hands on so being able to see the parts of the cell in a different way just made me understand everything about a cell and how everything works just that much better.
2. At what moment did you feel most distanced from the course? I felt most distanced from the unit when I had to figure how to put all the work that I did into a blog. To be really honest the blogging part really stressed me out because I wasn’t sure if I was doing what I needed to do.
3. What action that anyone took during this unit did you find most affirming and helpful? When the teacher actually explained to me how I had to post all my assignments into the same blog that is when I finally understood what I was doing.
4. What action that anyone took during this unit did you find most puzzling or confusing? Just the whole blogging thing again but I have a better understanding of it now.
5. What about this unit surprised you the most? I think learning about the different genotypes and phenotypes, also learning about the genetic disorders. These were the most interesting parts of the unit for me.
Ethical Issue: Cloning

Cloning is to produce a copy of or imitate. There are three different types of cloning; Therapeutic Cloning, Reproductive Cloning, and Recombinant DNA Technology or DNA Cloning. Therapeutic Cloning also known as embryo cloning is the producing of human embroyos for use in research. By harvesting stem cells that can later be used to study the development so that they are able to treat diseases. Reproductive Cloning is used to make an animal that has the same nuclear DNA as another animal either an animal in the past or one in the present. Recombinant DNA Technology or DNA Cloning is transfering DNA fragments from one organism to a self replicating genetic element.
Reproductive cloning is expensive and highly inefficient. Cloned animals have compromised immune functions. Higher rates of infection and other disorders have resulted with cloned animals. Clones have been known to die mysteriously and haven't been known to have long lifes. Of the mammals that have been cloned 30% of them were born with large offspring syndrome.
Cloning humans was said to be highly unethical and potentially dangerous by scientists and physicans. Cloned embryos are very likely to be born with birth defects. With animals it is different from humans because we dont have to worry about their mental develpment. Unlike humans where we thrive on mental develpment to function in todays society.
Many people have their own opinions on this issue. Some people might think that cloning will benefit us in the future while others believe it is unethical. Because there is such strong opinions, some for cloning and some against cloning, I dont believe that we will ever fully resolve the issue of weather we should clone humans.
Reproductive cloning is expensive and highly inefficient. Cloned animals have compromised immune functions. Higher rates of infection and other disorders have resulted with cloned animals. Clones have been known to die mysteriously and haven't been known to have long lifes. Of the mammals that have been cloned 30% of them were born with large offspring syndrome.
Cloning humans was said to be highly unethical and potentially dangerous by scientists and physicans. Cloned embryos are very likely to be born with birth defects. With animals it is different from humans because we dont have to worry about their mental develpment. Unlike humans where we thrive on mental develpment to function in todays society.
Many people have their own opinions on this issue. Some people might think that cloning will benefit us in the future while others believe it is unethical. Because there is such strong opinions, some for cloning and some against cloning, I dont believe that we will ever fully resolve the issue of weather we should clone humans.
Compendium Review 1-4


Outline
Chapters 1,2,3,4
Chapter 1
A. The characteristics of life
1. Acquiring materials and energy
2. Reproducing
3. Growing and Developing
4. Adapting to our environment
5. Life is an evolution
Chapter 2
A. Molecules along with atoms
B. Lipids
1. Oils and fats
2. Dietary Fats
Chapter 3
A. What is a cell?
1. Different parts of a cell
2. Roles they play
Chapter 4
A.Types of tissues
1. Four types of tissues
2. Details about each tissue
Chapters one through four, talked about many important things that has an affect on the human body. There were many important keys in this chapter about how you classify a living form from a non living thing. By taking on these forms you are classified as being a living object. All of them are very important to an individual such as growing and developing such as from a childhood to adolescent to then becoming an adult. Then reproducing creating a copy of two individuals and then insure that their own kind will continue. Another thing that makes us human is the ability that our body has to adapt to his or her environment. The most important one is that we change through time which is called evolution. With changing we are allowing ourselves to live longer lives then those who stay unchanged. Evolution has been going on since the beginning of life and will continue as long as life exists.In chapter two the book brings up water molecules along with atoms and isotopes. The best part was learning about the different oils and fats that you put in your body. I found out that fats are used for many different things in your body like long term storage, insulates against heat loss, and then forms a protected cushion around major organs. Then in the book it shows you an example of a food label and explains what calories you should intake. Also food manufacturers are required to list the amount of trans fat greater then that of .5 g in the nutrition for food.Chapter three is about what a cell is and shows many different pictures of what one looks like. In the pictures it shows many elements that help keep the cell functioning. An animal cell is different from that of a plant cell. Both eukaryotic and prokaryotic both have a plasma membrane which is the outer membrane that controls what goes in and out. Proteins play a major role in this as they decide what can enter and what can’t. All the cells also have cytoplasm, which is a semi fluid in the medium that has water and other types of molecules in it. Everything that is in a cell has an important role that allows certain functions within the body.The last chapter talked about the most important parts to the body, the four types of tissues, cell junctions and organ systems. The part that I was most interested in was the different types of epithelia and where it is found in humans. It is used for lining in lungs, blood vessels, small intestines, trachea, nose and the mouth. The reason why it is so important is because it protects, and it absorbs molecules and nutrients.
Chapters 1,2,3,4
Chapter 1
A. The characteristics of life
1. Acquiring materials and energy
2. Reproducing
3. Growing and Developing
4. Adapting to our environment
5. Life is an evolution
Chapter 2
A. Molecules along with atoms
B. Lipids
1. Oils and fats
2. Dietary Fats
Chapter 3
A. What is a cell?
1. Different parts of a cell
2. Roles they play
Chapter 4
A.Types of tissues
1. Four types of tissues
2. Details about each tissue
Chapters one through four, talked about many important things that has an affect on the human body. There were many important keys in this chapter about how you classify a living form from a non living thing. By taking on these forms you are classified as being a living object. All of them are very important to an individual such as growing and developing such as from a childhood to adolescent to then becoming an adult. Then reproducing creating a copy of two individuals and then insure that their own kind will continue. Another thing that makes us human is the ability that our body has to adapt to his or her environment. The most important one is that we change through time which is called evolution. With changing we are allowing ourselves to live longer lives then those who stay unchanged. Evolution has been going on since the beginning of life and will continue as long as life exists.In chapter two the book brings up water molecules along with atoms and isotopes. The best part was learning about the different oils and fats that you put in your body. I found out that fats are used for many different things in your body like long term storage, insulates against heat loss, and then forms a protected cushion around major organs. Then in the book it shows you an example of a food label and explains what calories you should intake. Also food manufacturers are required to list the amount of trans fat greater then that of .5 g in the nutrition for food.Chapter three is about what a cell is and shows many different pictures of what one looks like. In the pictures it shows many elements that help keep the cell functioning. An animal cell is different from that of a plant cell. Both eukaryotic and prokaryotic both have a plasma membrane which is the outer membrane that controls what goes in and out. Proteins play a major role in this as they decide what can enter and what can’t. All the cells also have cytoplasm, which is a semi fluid in the medium that has water and other types of molecules in it. Everything that is in a cell has an important role that allows certain functions within the body.The last chapter talked about the most important parts to the body, the four types of tissues, cell junctions and organ systems. The part that I was most interested in was the different types of epithelia and where it is found in humans. It is used for lining in lungs, blood vessels, small intestines, trachea, nose and the mouth. The reason why it is so important is because it protects, and it absorbs molecules and nutrients.
Compendium Review 18-21


Outline
Chapter 18
A. Chromosomes and the cell cycle
1. sex chromosomes
2. Mitosis
3. Phases of Mitosis
4. Meiosis
5. Two stages of Meiosis
Chapter 19
A. Cancer Cells
1. Different Types
2. Causes of Cancer
Chapter 20
A. Genetic Inheritance
B. DNA, RNA
Chapter 21
A.DNA Fingerprinting
1. How it has helped solve crimes
Through out chapters 18 through 21 the book discussed many different things from chromosomes of a cell to that of genetics and inheritance. A lot of the chapters in this section are important to understand because of genetic disorders to cancer and how it can be heredity. In the first chapter it discusses how many chromosomes a person has and what sex chromosomes a male has that is different from a female. Males have X and Y sex chromosomes and females have two X chromosomes. Then later it goes into detail about mitosis and meiosis. In mitosis it has the same number and kind of chromosomes as the cell that later divides it and also has four different stages that the cell goes through. The four different stages are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telephone each phase goes right onto the other without any interruption. Meiosis involves two divisions which involve four daughter cells and then each daughter cell has a different chromosome that means half as many parents’ cells are involved. The two different cell divisions of meiosis is meiosis l and meiosis ll. So what is the difference from mitosis and meiosis? Mitosis is the most common out of the two because it takes part in all tissues during growth and repair. While Meiosis only happens in the reproductive organs and then produces the gametes (the sex cell, the egg or a sperm).Chapter 19 is about cancer cells which was very interesting because so many people die each year from this. The cancer cell keeps on dividing for an unlimited number of times unlike other cells that divide about 60-70 times and then they stop dividing and die off. What are the different types of cancers? Cancers of the blood are classified as leukemia, and then there are cancers in the muscle and connective tissue which are known as sarcomas. Cancers of the epithelial tissues are called Carcinomas which includes skin, breast, liver, pancreas, intestines, lung, prostate and thyroid. Cancers of the lymphatic tissue are lymphomas. The causes of cancer are not fully understood however the environment plays a role in risk factors. Heredity plays the biggest role in cancer especially certain types. Genes that you inherit can play a big role in what types of cancers are common in your family. Other causes that you might not expect are ultraviolet radiation in sunlight and tanning lights which can increase the risks of skin cancer. Organic chemicals such as tobacco smoke, pollutants and viruses can increase the risk factor.Chapters 20 talks about genetic inheritance, DNA and RNA. It explains how genotypes and phenotypes form. Each gene can figure out by the genes that your parents have which genes you will inherit from each of your parents. How some people have a widow’s peak while others might just have a straight hairline. To those individuals that have thousands of freckles and those of us that have no freckles. Other things that they are now being able to find out is if your child could possible end up having a genetic disorder before birth.Chapter 21 discusses a big change that has helped solve crimes and that being DNA testing. Cops are able to catch criminals that are involved in a crime because of DNA fingerprinting from blood or tissue at crime scenes. It also helps with identifying bodies. For instance it was a huge help in identifying the victims of the September 11 terrorist attacks in the United States.
Chapter 18
A. Chromosomes and the cell cycle
1. sex chromosomes
2. Mitosis
3. Phases of Mitosis
4. Meiosis
5. Two stages of Meiosis
Chapter 19
A. Cancer Cells
1. Different Types
2. Causes of Cancer
Chapter 20
A. Genetic Inheritance
B. DNA, RNA
Chapter 21
A.DNA Fingerprinting
1. How it has helped solve crimes
Through out chapters 18 through 21 the book discussed many different things from chromosomes of a cell to that of genetics and inheritance. A lot of the chapters in this section are important to understand because of genetic disorders to cancer and how it can be heredity. In the first chapter it discusses how many chromosomes a person has and what sex chromosomes a male has that is different from a female. Males have X and Y sex chromosomes and females have two X chromosomes. Then later it goes into detail about mitosis and meiosis. In mitosis it has the same number and kind of chromosomes as the cell that later divides it and also has four different stages that the cell goes through. The four different stages are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telephone each phase goes right onto the other without any interruption. Meiosis involves two divisions which involve four daughter cells and then each daughter cell has a different chromosome that means half as many parents’ cells are involved. The two different cell divisions of meiosis is meiosis l and meiosis ll. So what is the difference from mitosis and meiosis? Mitosis is the most common out of the two because it takes part in all tissues during growth and repair. While Meiosis only happens in the reproductive organs and then produces the gametes (the sex cell, the egg or a sperm).Chapter 19 is about cancer cells which was very interesting because so many people die each year from this. The cancer cell keeps on dividing for an unlimited number of times unlike other cells that divide about 60-70 times and then they stop dividing and die off. What are the different types of cancers? Cancers of the blood are classified as leukemia, and then there are cancers in the muscle and connective tissue which are known as sarcomas. Cancers of the epithelial tissues are called Carcinomas which includes skin, breast, liver, pancreas, intestines, lung, prostate and thyroid. Cancers of the lymphatic tissue are lymphomas. The causes of cancer are not fully understood however the environment plays a role in risk factors. Heredity plays the biggest role in cancer especially certain types. Genes that you inherit can play a big role in what types of cancers are common in your family. Other causes that you might not expect are ultraviolet radiation in sunlight and tanning lights which can increase the risks of skin cancer. Organic chemicals such as tobacco smoke, pollutants and viruses can increase the risk factor.Chapters 20 talks about genetic inheritance, DNA and RNA. It explains how genotypes and phenotypes form. Each gene can figure out by the genes that your parents have which genes you will inherit from each of your parents. How some people have a widow’s peak while others might just have a straight hairline. To those individuals that have thousands of freckles and those of us that have no freckles. Other things that they are now being able to find out is if your child could possible end up having a genetic disorder before birth.Chapter 21 discusses a big change that has helped solve crimes and that being DNA testing. Cops are able to catch criminals that are involved in a crime because of DNA fingerprinting from blood or tissue at crime scenes. It also helps with identifying bodies. For instance it was a huge help in identifying the victims of the September 11 terrorist attacks in the United States.
What Is Genetics??

 For the genetics lab we had to go to two different sites to work on labs. One was the dragon genetics lab and the other one was the punnett square. The dragon genetics explained the relationship between phenotypes and genotypes, and then you create physical changes in the dragons. Then I went and worked on the punnett square that took a lot more time for me to finally understand what I was suppose to do. You had to make a cross between the two flies, homozygous with long wings and homozygous with vestigial winged flies. By doing these labs it allowed you to get more familiar with genetic inheritance and how you receive the genes that you do.What is genetic inheritance? Inheritance is the traits that you receive from each one of your parents. Everyone has two copies of every gene, one inherited from the mother and one inherited from the father which is known as alleles. So if we inherit our genes from our parents they why don’t we look identical to our parents. It is because we inherit half of our father’s chromosomes and half of our mothers. There are important parts that you should know in order to understand how to do a punnett square and doing the genetics lab. During the dragon genetics lab you got to see recessive and dominant genes. Recessive inheritance is both parents have a normal gene and a faulty, recessive gene. Parents are not affected by the faulty gene, but their offspring is affected. A dominant inheritance means a parent has a single faulty dominant gene. This overpowers the counterpart and has an affect on the parent. When the parent is affected and mates with a non affected and non carrier mate the offspring could or could not be affected. Genotypes and phenotypes are genes of an individual. Phenotypes are an individual’s physical or observable characteristics.
For the genetics lab we had to go to two different sites to work on labs. One was the dragon genetics lab and the other one was the punnett square. The dragon genetics explained the relationship between phenotypes and genotypes, and then you create physical changes in the dragons. Then I went and worked on the punnett square that took a lot more time for me to finally understand what I was suppose to do. You had to make a cross between the two flies, homozygous with long wings and homozygous with vestigial winged flies. By doing these labs it allowed you to get more familiar with genetic inheritance and how you receive the genes that you do.What is genetic inheritance? Inheritance is the traits that you receive from each one of your parents. Everyone has two copies of every gene, one inherited from the mother and one inherited from the father which is known as alleles. So if we inherit our genes from our parents they why don’t we look identical to our parents. It is because we inherit half of our father’s chromosomes and half of our mothers. There are important parts that you should know in order to understand how to do a punnett square and doing the genetics lab. During the dragon genetics lab you got to see recessive and dominant genes. Recessive inheritance is both parents have a normal gene and a faulty, recessive gene. Parents are not affected by the faulty gene, but their offspring is affected. A dominant inheritance means a parent has a single faulty dominant gene. This overpowers the counterpart and has an affect on the parent. When the parent is affected and mates with a non affected and non carrier mate the offspring could or could not be affected. Genotypes and phenotypes are genes of an individual. Phenotypes are an individual’s physical or observable characteristics.The Parts and Functions of the Microscope...


Does the microscope have any effect on today’s society? There are many different types of microscopes from inverted, forensic, industrial and these are just a few. Microscopes are an invaluable tool that is used in today’s research and education. It has helped major discovers in biology, medicine and materials research that are based on the advances that happens with the microscope. Without the microscopes there would probably be no new discovers on medical issues or even in the science field.The microscope has made many changes since the first discovery of it in 1590. It was the first light microscope that was invented by two Dutch spectacle makers, Zaccharias Janssen and his son Hans. They first discovered it by experimenting with several different lenses in a tube; they later found out that objects appear enlarged. But the major father of the microscope would have to be Anton Van Leeuwenhoek of Holland. He worked in a goods store which happened to have magnifying glasses; this helped him in building his microscopes. Anton was the first to discover many things with the microscope such as bacteria, yeast plants, the teeming life in a drop of water, and the blood corpuses in capillaries. During Aton's lifetime he used the lenses to do studies on varies things both living and none living and then later wrote his findings down. Fewer studies were then found on the microscope till the 19th century when the fine optical equipment was invented by Charles A Spencer. Later on in the 1930s the electron microscope was introduced, this helped a great deal. They allowed you to view objects as small as the diameter of an atom. Even though this is just a couple of findings with the microscope you can just see what a huge affect it has on today’s lives.There are many different parts to a microscope the most important thing is to figure out the different parts and then learn what each one does. When I had to learn all the different parts for my biology class, it was best for me to find a picture of the microscope and label the different parts. Each part is just important as the next, if you don’t do a certain thing right then you will not see the images, or will not be able to find it. These are the most important parts that you should know before you start using a microscope. The stage where you set your slides on it after you have chosen the slide you are going to be viewing. Condenser focus knob: this control is used to precisely adjust the vertical height of the condenser. Fine focus control allows for precise focusing of the slide. Objective Lenses are usually always consisting of 4x, 10x, 40x, and 100x power. The shortest lens is the lowest power while the longest is the greatest power. Iris or Diaphragm is the function of transparency in the slide and the degree of contrast you desire. The last piece that is very important the ocular or also known as the eyepiece this contains two or more pieces to bring the images into focus for the eye to see. While dealing with a microscope it is best to look at the microscope while you adjust these certain pieces, choose the slide your going to look at, scanning the lens in place, specimen centered then open iris before doing this, and then start the stage at the top position. The next things are best to do while you are looking through the eye piece: use your focus, set your iris the degree of contrast you want to use, adjust the fine focus, and after you have set the fine focus center your image.
Unit One: Build A Cell (Stages of the Cell Being Completed)





 Introduction: This is a model of a cell that I created using items from around my house. Here are the items I used listed below and which part of the cell they represent.
Introduction: This is a model of a cell that I created using items from around my house. Here are the items I used listed below and which part of the cell they represent.Cell membrane- A blue plastic bowl and cut the lip off of it. Inside the bowl I filled it with sand to make it look like the cytoplasm.
Nucleus with nuclear membrane- Styrofoam ball that I cut in half, then cut a triangle out of it and painted it purple.
Endoplamic reticulum- drew rough and smooth edges on a piece of construction paper.
Golgi apparatus- plastic fishing worms that I cut to shape and size that I wanted.
Lysosomes and vesicles- A fishing worm that I cut the end off.
Mitochondria- A kidney bean that I drew designs on.
Cillia or flagella made of microtubles- plastic craft string that I cut to size.
Unit One Building a Cell Project
 List of the parts of the cell by the numbers on the cell model.
List of the parts of the cell by the numbers on the cell model.1) Cell Membrane: The outer surface of a cell that controls molecules entrance and exit.
2) Nucleus With Nuclear Membrane: Two membranes that enclose a flattened sac and are connected at the nucleor pore. It is enmeshed in a group of filaments for strength.
Endoplasmic reticulum: A complex network of membrane enclosed spaces
3) Rough ER: bordered by ribosomes that contain large amounts of RNA.
4) Smooth ER: These membranes smooth because they have no ribosomes.
5) Golgi Apparatus: consists of a stack of flat baglike structures which store and eventually release various products from the cell.
6) Lysosomes and Vesicles: small, round bodies containing many different enzymes. They break down many substances. For example they help white blood cells break down harmful bacteria.
7) Mitochondria: The power producers of the cell which are sausage-shaped structures. They produce almost all the energy the cell needs to live and do its work.
8)Cilia or Flagella Made of Microtubules: cylinders of protein molecules and they function to determine cell shape and variety of cell movements.
Conclusion: My model shows all the parts within a cell. By creating all the different parts by using things around the house gave me a good understanding of what the cell parts look like. I also have a better understanding of their function.
its all about me.....
Hello, my name is Brandi and I'm a very shy person and really like to keep to myself. I enjoying listening to any kind of music as long as it has a good sound and a good singer. The past two years that I attended Yavapai College I was a member of the womens basketball team. But now I have decided to just focus on working and school. The reasons for taking human biology are I might use the information I learn in my teaching profession. I previously took environmental biology and didnt do as well as i would have liked so I thought human biology would be a lot more interesting to me. I hope to gain the knowlege that I need about the different genetic disorders, cells, and anything else that would help me along the way through the education process.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)